The Rise of Telehealth: How Insurance Companies Adapted During the Pandemic
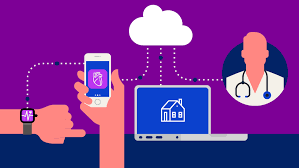
The COVID-19 pandemic transformed healthcare delivery, leading to an unprecedented rise in telehealth services. With lockdowns and social distancing measures in place, people turned to virtual doctor visits to safely access healthcare from home. In response, insurance companies made significant changes to accommodate this shift, ensuring patients had access to remote care. This adaptation not only revolutionized patient access but also reshaped the future of healthcare. Here’s a look at how insurance companies adjusted to the rapid expansion of telehealth and what this means going forward.
1. Rapid Expansion of Telehealth Coverage
Before the pandemic, many insurers covered limited telehealth services, primarily for rural areas or specialized care. But in 2020, insurance companies quickly expanded their telehealth coverage to accommodate the surge in demand. Key adaptations included:
- Broad Coverage Across Specialties: Insurers extended telehealth coverage to include primary care, mental health, urgent care, chronic disease management, and even specialty services like physical therapy and dermatology.
- State and Federal Mandates: State and federal mandates encouraged insurers to cover telehealth on par with in-person visits, leading to wider acceptance and support from insurance companies across the U.S.
These adaptations were especially crucial for patients in rural areas or those with limited access to in-person facilities, making healthcare more equitable.
2. Waiving Cost-Sharing and Copayments
To encourage the use of telehealth during the pandemic, many insurers waived copays, deductibles, and coinsurance for telehealth visits, including COVID-19 screenings. Major insurers such as UnitedHealthcare, Cigna, and Blue Cross Blue Shield implemented temporary policies to reduce or eliminate out-of-pocket costs for telehealth, helping reduce financial barriers for patients who were new to virtual care.
- Financial Accessibility: By reducing financial costs, insurers made telehealth services accessible to millions, enabling patients to prioritize their health without fearing high costs.
- Public Health Impact: Waiving costs helped alleviate the strain on healthcare facilities, ensuring that patients who needed urgent in-person care could access it without overwhelming emergency services.
While some of these waivers have since been lifted, the temporary relief encouraged many patients to try telehealth, broadening its acceptance across the country.
3. Integration of Mental Health Telehealth Services
The pandemic caused a rise in mental health concerns, from stress and anxiety to depression. Recognizing this need, insurance companies rapidly increased access to mental health telehealth services. They not only expanded coverage but also contracted with popular mental health platforms, such as Talkspace and BetterHelp, allowing patients to access licensed therapists and psychiatrists remotely.
- Mental Health Parity: Insurers embraced mental health telehealth to ensure patients received necessary support, aligning with federal mental health parity laws.
- Long-Term Impact: This integration helped destigmatize mental health care by making it accessible from home, a trend that has continued beyond the pandemic.
By making mental health services available remotely, insurance companies helped millions of patients manage stress and anxiety during challenging times.
4. Partnerships with Telehealth Platform
To keep up with demand, insurance companies partnered with telehealth platforms like Teladoc, Amwell, MDLIVE, and Doctor on Demand. These collaborations enabled insurers to quickly offer virtual care without the need for a physical infrastructure overhaul.
- Streamlined Services: By partnering with telehealth platforms, insurers could offer access to a variety of specialties and on-demand services.
- Quality Control and Accessibility: These partnerships allowed insurers to ensure that patients received quality care while navigating an expanded network of providers.
The partnerships also brought new telehealth services to markets where virtual care options were previously limited, providing a more extensive range of providers.
5. Adjusting Reimbursement Policies for Providers
Insurance companies updated their reimbursement policies to encourage healthcare providers to offer telehealth. Early on, many insurers increased or matched in-person visit reimbursements to make telehealth services financially viable for healthcare providers.
- Reimbursement Parity: Some states mandated telehealth reimbursement parity, which led insurers to reimburse virtual visits at the same rate as in-person visits, making telehealth financially sustainable for providers.
- Encouraging Provider Participation: These reimbursement changes ensured that providers could continue serving patients without revenue loss, supporting the continuity of care during the pandemic.
By offering reimbursement parity, insurers incentivized providers to adopt telehealth, allowing more patients to access care remotely.
6. Extended Flexibility and Cross-State Licensing
During the pandemic, regulatory agencies and insurers introduced temporary policies allowing healthcare providers to practice across state lines through telehealth. This flexibility helped address provider shortages and allowed patients in underserved areas to access care.
- Cross-State Licensing and Coverage: Insurers adjusted policies to enable cross-state telehealth, allowing out-of-state providers to treat patients, especially in mental health, a specialty with a national shortage.
- Future of Licensing Flexibility: Although some of these changes were temporary, the positive impact has led to discussions about longer-term solutions, potentially reshaping state licensing regulations to allow for greater telehealth access.
By facilitating cross-state telehealth, insurers helped improve patient access to specialized services that might not be available locally.
7. Permanent Changes and the Future of Telehealth
Although some temporary telehealth policies have ended, insurers continue to embrace virtual care due to its convenience and cost-effectiveness. The pandemic accelerated telehealth’s acceptance, making it a core part of healthcare delivery moving forward. Long-term changes likely include:
- Mental Health and Primary Care Access: Expanded telehealth coverage, especially for mental health and primary care, is here to stay as insurers recognize its long-term value.
- Increased Patient Demand: Patient comfort with telehealth has grown, and insurers are adapting to meet the increased demand with permanent coverage options.
- Hybrid Care Models: Insurers are supporting hybrid models where patients can choose between in-person and virtual visits based on their needs, adding flexibility and choice to healthcare.
Conclusion
The pandemic changed the landscape of healthcare, with telehealth emerging as a critical service for millions of patients. Insurance companies adapted by expanding telehealth coverage, partnering with virtual platforms, and implementing policies that encourage both patients and providers to use virtual care. These changes not only improved access to healthcare but also demonstrated the value of telehealth in maintaining continuity of care during challenging times. With insurers increasingly recognizing the benefits of telehealth, it’s clear that virtual healthcare is here to stay, bringing more accessible and flexible options for patients nationwide.
Leave a Reply